Shoulder Labrum Reconstruction
Home / Area of Specialty / Shoulder / Shoulder Labrum Reconstruction
What is Shoulder Labrum Reconstruction?
Shoulder Labrum Reconstruction is a surgery to repair the torn labium in the shoulder. The torn labrum is usually caused by shoulder dislocation or by a chronic shoulder instability. Shoulder labral surgery such as shoulder bankart repair, labral debridement and SLAP repair are techniques used to treat this condition.
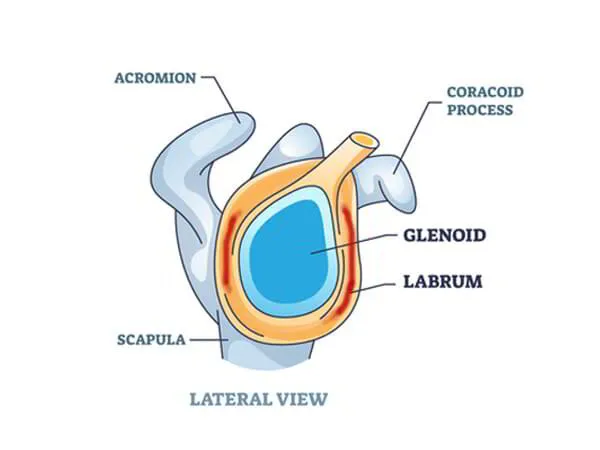
Labrum repair surgery is a procedure recommended
for treating tears of the labrum, which is a rim of
cartilage that attaches around the shoulder joint
and provides stability. The surgeon uses sutures to
reattach the labrum to its normal position around
the shoulder joint. The surgeon also tightens up
junctures in the shoulder capsule, as well as
loosens soft tissues supporting the biceps tendon,
which overlaps the edge of the labrum leading to the
shoulder bone when the arm is raised. All this
serves to stabilize the shoulder joint and restore
strength and range of motion.
Who needs Shoulder Labrum Reconstruction?
Bankart injuries are common among contact sports and repetitive overhead activities, as well as a result of falls on the shoulder. Bankart tears make the shoulder joint unstable; it may dislocate multiple times, feel loose, have a loss of strength and cause pain or clicking. In more serious cases involving extreme instability, there can be paralysis, loss of sensation and severe pain.
Shoulder instability is a common shoulder problem with age that can result from injury or degeneration. Some of the possible symptoms include weakness, pain, stiffness, muscle spasms, and difficulty moving the arm.
Tests and Diagnosis for Shoulder Labrum Reconstruction
Your doctor will conduct a series of tests and examinations to detect the symptoms of a labral tear. The doctor may suspect a labral tear based on your symptoms and medical history. If a labral tear is suspected, the doctor may recommend an X-ray, CT scan or MRI scan. A diagnosis can also be confirmed through shoulder arthroscopy.
What are the treatments for Shoulder Labrum repair?
Non-surgical Treatment
If conservative treatment fails to relieve shoulder instability, shoulder reconstruction surgery may be required.
Surgical Treatment
The shoulder joint is a ball and socket joint. Due to injury or wear and tear, the ligaments holding the joint in place may get stretched or torn leading to instability of the joint. This can result in pain and loss of motion in the shoulder. Shoulder reconstruction procedure is done only if the problem does not respond to non-operative treatments like physical therapy, anti-inflammatory medications, injections, etc. In this procedure, any damaged ligaments are repaired so that normal movement and stability can be restored. Surgeon may use tiny pinpointed incisions (arthroscopy) or large surgical incisions through which arthroscopic instruments are placed to perform this surgery.
After shoulder Labrum repair surgery, you will be immobilized in a sling for 4 to 6 weeks to facilitate healing. You may have slight pain after surgery for which pain medications are prescribed. Apply ice packs on the shoulder to reduce swelling. You can use a pillow under the shoulder while lying in bed.
Shoulder Labrum repair Post-operative precautions
Following the surgery, your shoulder is immobilized with a sling for a few days.
Avoid heavy lifting and driving during the first six weeks.
You will be given specific instructions regarding activity and a rehabilitation program of strengthening exercises.
After shoulder labrum reconstruction, common treatments include ice, electrical stimulation, massage therapy and other hands-on techniques.
Passive range of motion exercises are also initiated in the postoperative phase.
Active range of motion exercises are started about 6 weeks after the repair.
Athletes can return to sports in about three months.
What are the risks & complications?
Some common complication associated are
- Nerve injury
- Wound infection
- Tear of the repair
- Shoulder stiffness
- Recurrence of instability
- Poor positioning of anchor suture
- Failure of the repair