Partial Knee Replacement
Home / Area of Specialty / Knee / Partial Knee Replacement
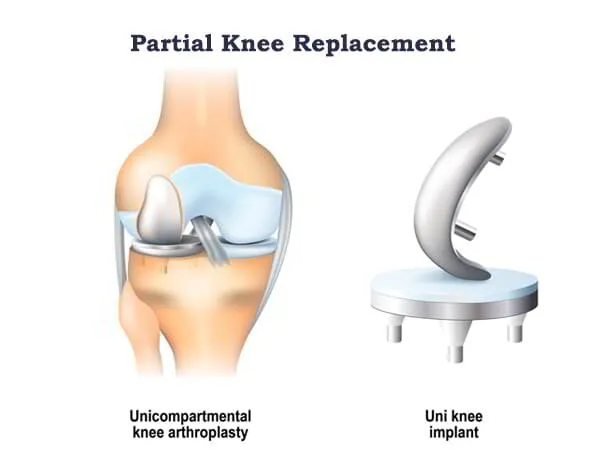
What is Partial Knee Replacement?
Partial knee replacement also referred as Unicompartmental knee replacement is a minimally invasive surgical procedure to repair damaged ligaments or cartilage in the knee. The damaged area is surgically replaced with a prosthesis (artificial joint) and only the damaged compartment is replaced instead of an entire joint.
The knee joint is made up of various parts. There are three major compartments: the front compartment between the kneecap and thigh bone, the middle (or medial) compartment on the inside of the knee, and the back (or lateral) compartment on the outside of the knee joint.
Who needs Partial Knee Replacement?
If you have joint disease caused by painful osteoarthritis or traumatic injury, meaning a breakdown of the cartilage, ligament damage and significant knee stiffness that cushions the knee joint and keeps it stable, you may be a candidate for what is called the partial knee replacement. If your symptoms have not improved with medications, injections, and physical therapy, you may be a candidate for unicompartmental knee replacement, your arthritis must be limited to one compartment in the knee.
Surgical Procedure of Partial knee replacement
Using a minimally invasive procedure, the surgeon removes only the damaged part of your meniscus. This is then replaced with a metal implant. Then, the surgeon reshapes the thighbone and shinbone, creating an opening where the implant will be inserted into the bone. The plastic component is placed into this opening, which is then secured in place using bone cement. Next, the damaged region of the femur or thighbone is removed to accommodate the new metal component, which is fixed in place using bone cement. The knee-cap is then taken through a range of movements. The muscles and tendons are then repaired and incisions are closed.
What are the risks and complications associated?
Complications are rare, but they can include infection, bleeding, blood clots, nerve and blood vessel damage, ligament injuries, patella dislocation, loosening of the implant and wear of the plastic liner.