Lateral Collateral Ligament Surgery
Home / Area of Specialty / Knee / Lateral Collateral Ligament Surgery
Dr. Pradyumna R carefully evaluate your conditions and symptoms associated to your knee pain and knee injuries, based on the diagnostic report and scan he would suggest if so, you are a candidate for Lateral Collateral Ligament Surgery procedure, he is an highly experienced knee treatment specialist provides diagnosis as well as surgical and nonsurgical treatment options at Bangalore Orthopaedic Clinic, in BTM Layout, Bangalore.
If you have any queries or would like to schedule an appointment for Lateral Collateral Ligament Surgery procedure, or knee pain treatment consultation, please call +919113025188.
What is a Lateral Collateral Ligament Injuries?
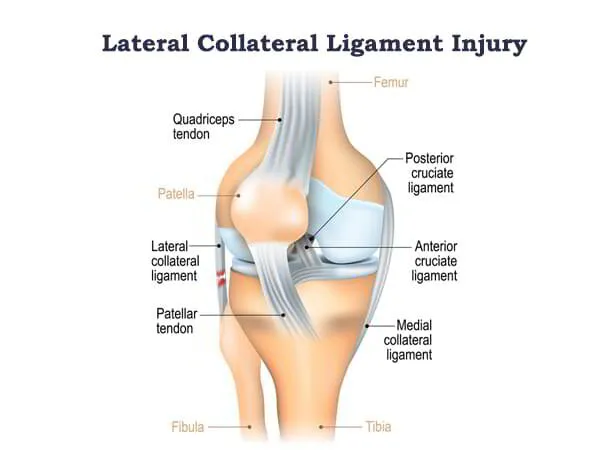
The lateral collateral ligament (LCL) is a major structure of the knee joint that restricts excessive motion in the sideways direction of the knee. It is the strongest lateral ligament of the knee and connects the femur of the upper leg to the lower leg, called tibia and fibula.
The LCL is a band of tissue that connects the knee joint to the leg. An LCL injury can occur in several ways. Torn or injured LCL may cause instability to the knee that can be either reconstructed or repaired to regain the strength and movement of the knee.
What is LCL Reconstruction Surgery?
LCL reconstruction is a surgical procedure to repair or replace the torn or damaged tissue in the knee's lateral collateral ligament with a piece of tendon or strip of cartilage. This can be performed by grafting a piece of hamstring tendon onto the torn LCL.
What causes of LCL Injuries?
An injury to the LCL is a very common problem for athletes who play running or jumping sports. The lateral collateral ligament may also be injured during contact sports or a direct blow to the knee. A torn LCL may result in pain, swelling, and instability of the knee.
What the test of LCL Injuries diagnosis?
The diagnosis of a tear in the Lateral Collateral Ligament is typically done first by a physical examination; however, MRI scans and X-ray imaging may be employed to confirm the diagnosis.
What are the treatments for LCL Injuries?
Non-Surgical Treatment
The tear of the LCL occurs between the upper and lower pole attachments. The injury can also be present at the middle of the ligament.
A non-surgical treatment may include rest, ice, elevation, bracing and physical therapy to help reduce swelling and regain activity, as well as strengthen and improve the flexibility of the knee.
Surgical Treatment
The LCL (lateral collateral ligament) is a ligament that runs across the side and back of the knee. It causes the knee to flex and stabilize the joint. If this ligament is torn, it must be reconstructed to restore stability to the knee. This can be done either from your own body or from a tissue bank via allograft. In this procedure, the graft is stitched or sutured into place, just as the torn ligament was previously. The hamstrings are commonly used as an autograft for this procedure, as hamstring tendon removal does not affect leg strength or activity levels.
The LCL reconstruction procedure is performed through an open incision and not arthroscopically. Specifically, the femur and tibia are precisely drilled to form tunnels for the ligament to be repaired. A graft (piece of tissue) from a non-weight bearing area of your own body is then attached to these pieces of bone. The knee is put in a brace for 6-8 weeks for it to heal fully before you can begin physical therapy.
Postoperative care following LCL Reconstruction
You will have your leg elevated above heart level to reduce bleeding and swelling. Keep your leg elevated as much as possible while resting on a flat surface or with pillows. You may be advised to use crutches for six weeks if you have a history of knee problems.
Apply ice packs and take prescription medications to relieve inflammation, soreness, bruising, and joint stiffness. Watch for signs of infection [pus, redness, warmth, but remember that swelling after surgery is common.
Finally, plan to attend outpatient physical therapy [PT] as instructed by your surgeon.
What the risks and complication?
Potential risks and complications include. Chronic pain, knee weakness, and knee instability are possible complications associated with LCL reconstruction. In rare cases peroneal nerve injury may occur.
For more information on LCL tears, injuries or lateral collateral ligament surgery or LCL reconstruction and the treatment options LCL sprain and LCL injuries available, please call +919113025188. Dr. Pradyumna R, orthopedic knee specialitst serving BTM Layout, Bangalore City.